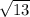To answer this, you basically use Pythagoras' Theroem, but instead of:
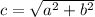
it will be :
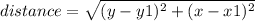
So you are finding the squareroot of the (difference in y coordinates)² plus (difference in x coordinates) ²:
x is the x-coordinate of (0, -1) (so x = 0)
y is the y-coordinte of (0, -1) ( so y = -1)
x1 is the x coordinate of (3, -3) ( so x1 = 3)
y1 is the y coordinate of (3, -3) (so y1 = -3)
--------------------------------------------------
Now, lets find the distance between the two points, by substituting all of this values into the equation at the top:
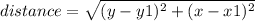 (substitute in values)
(substitute in values)
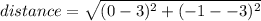 (simplify: note -1 - - 3 = -1 + 3)
(simplify: note -1 - - 3 = -1 + 3)
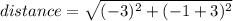 (simplify)
(simplify)
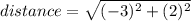 (now square the numbers)
(now square the numbers)
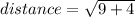 (simplify)
(simplify)
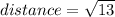
___________________________________________
Answer:
C.