Answer:
77.6%
Step-by-step explanation:
Parameters given:
Number of moles of H₂ = 1 mole
Actual yield = 14g
Equation of the reaction:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Solution
From the statement of the problem, we have been given the actual yield that was obtained during the laboratory procedure. Now, we find the theoretical yield and this would lead us to the percentage yield.
Percentage yield =
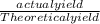 x 100
x 100
Theoretical yield:
From the stoichiometeric equation:
2moles of H₂ produced 2 moles of water
Hydrogen gas the limiting reactant and it is in short supply,
Therefore, 1 mole of water would be produced by 1 mole of hydrogen gas.
We use this to estimate the mass of the water that would be produced:
mass of water = number of moles of water x molar mass of water
Molar mass of H₂O = (2x1) + 16 = 18gmol⁻¹
mass of water = 1 mol x 18gmol⁻¹ = 18g
This is the theoretical yield
Percentage yield =
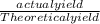 x 100
x 100
Percentage yield =
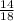 x 100 = 77.6%
x 100 = 77.6%