Answer: Mass of nitrous oxide used is 264 grams and mass of oxygen gas used is 96 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
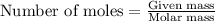 ....(1)
....(1)
- For a: Combustion of ethylene in nitrous oxide
The chemical equation for the combustion of ethylene in nitrous oxide follows the equation:
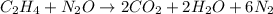
By stoichiometry of the reaction;
6 moles of nitrous oxide are required for the complete combustion of ethylene molecule.
Calculating the mass of nitrous oxide using equation 1:
Molar mass of nitrous oxide = 44 g/mol
Moles of nitrous oxide = 6 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
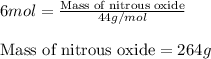
Thus, 264 grams of nitrous oxide are required for the complete combustion of ethylene.
- For b: Combustion of ethylene in air
The chemical equation for the combustion of ethylene in air follows the equation:
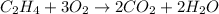
By stoichiometry of the reaction;
3 moles of oxygen are required for the complete combustion of ethylene molecule.
Calculating the mass of oxygen using equation 1:
Molar mass of oxygen = 32 g/mol
Moles of oxygen = 3 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
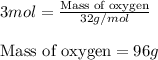
Thus, 96 grams of oxygen are required for the complete combustion of ethylene.