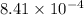Answer:
For a: The equilibrium concentration of CO and
 are 0.24 M and 0.32 M.
are 0.24 M and 0.32 M.
For b: The value of
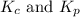 are 1.5625 and
are 1.5625 and
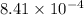
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Volume of container = 5 L
Initial moles of CO = 1.8 moles
Initial concentration of CO =
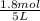
Initial moles of
 = 2.2 moles
= 2.2 moles
Initial concentration of
 =
=
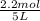
Equilibrium moles of
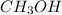 = 0.6
= 0.6
Equilibrium concentration of
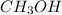 =
=
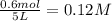
The chemical equation for the formation of methanol follows:
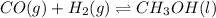
t = 0
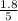
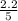 0
0
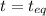
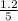
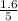
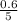
So, the equilibrium concentration of CO =
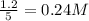
The equilibrium concentration of
 =
=
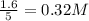
The expression of
 for the given chemical reaction follows:
for the given chemical reaction follows:
![K_c=([CH_3OH])/([CO][H_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/egbmnjoy5wkpz32257d34hh4knfry596vk.png)
We are given:
![[CH_3OH]=0.12mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/jadkb5k40t9akmmfl1cfduebqm42zx0v2y.png)
![[CO]=0.24mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cgljjts858cuan7eqztnbqgik98345wwak.png)
![[H_2]=0.32mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/od4416s9x4ioq2m2ijxvq2vcin6qq1qs73.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
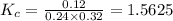
Relation of
 with
with
 is given by the formula:
is given by the formula:
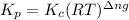
Where,
 = equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
= equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
 = equilibrium constant in terms of concentration = 1.5625
= equilibrium constant in terms of concentration = 1.5625
R = Gas constant =
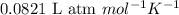
T = temperature = 525 K
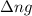 = change in number of moles of gas particles =
= change in number of moles of gas particles =
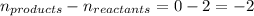
Putting values in above equation, we get:
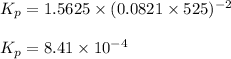
Hence, the value of
 are 1.5625 and
are 1.5625 and