Answer:
For 1: The volume of carbon monoxide required to produce given amount of methanol is 11.9 L.
For 2: The volume of oxygen required to form given amount of water is 7.77 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
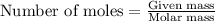 ......(1)
......(1)
For methanol:
Given mass of methanol = 19.3 g
Molar mass of methanol = 32 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
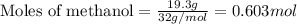
The chemical reaction of formation of methanol from carbon monoxide follows:
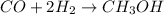
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of methanol is produced from 1 mole of carbon monoxide.
so, 0.603 moles of methanol will be produced from =
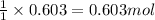 of carbon monoxide.
of carbon monoxide.
To calculate the volume of carbon monoxide, we use the equation given by ideal gas:
PV = nRT
where,
P = Pressure of carbon monoxide = 676 mmHg
V = Volume of carbon monoxide = ? L
n = Number of moles of carbon monoxide = 0.603 mol
R = Gas constant =
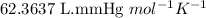
T = Temperature of carbon monoxide = 212 K
Putting values in above equation, we get:
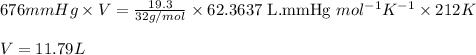
Hence, the volume of carbon monoxide required to produce given amount of methanol is 11.9 L.
Calculating the moles of water by using equation 1, we get:
Given mass of water = 12.5 g
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
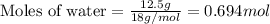
The chemical reaction of formation of water from oxygen and hydrogen follows:
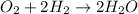
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of water is produced from 1 mole of oxygen gas.
so, 0.694 moles of water will be produced from =
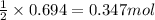 of oxygen gas.
of oxygen gas.
At STP:
1 mole of a gas occupies 22.4 L of volume.
So, 0.347 moles of oxygen gas will occupy =
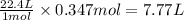
Hence, the volume of oxygen required to form given amount of water is 7.77 L.