Answer:
The center of mass of the two-ball system is 7.05 m above ground.
Step-by-step explanation:
Motion of 0.50 kg ball:
Initial speed, u = 0 m/s
Time = 2 s
Acceleration = 9.81 m/s²
Initial height = 25 m
Substituting in equation s = ut + 0.5 at²
s = 0 x 2 + 0.5 x 9.81 x 2² = 19.62 m
Height above ground = 25 - 19.62 = 5.38 m
Motion of 0.25 kg ball:
Initial speed, u = 15 m/s
Time = 2 s
Acceleration = -9.81 m/s²
Substituting in equation s = ut + 0.5 at²
s = 15 x 2 - 0.5 x 9.81 x 2² = 10.38 m
Height above ground = 10.38 m
We have equation for center of gravity
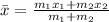
m₁ = 0.50 kg
x₁ = 5.38 m
m₂ = 0.25 kg
x₂ = 10.38 m
Substituting
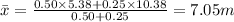
The center of mass of the two-ball system is 7.05 m above ground.