Answer:
The reaction isn't yet at equilibrium. The overall reaction will continue to move in the direction of the products.
Assumption: this system is currently at
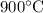 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
One way to tell whether a system is at its equilibrium is to compare its reaction quotient
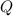 with the equilibrium constant
with the equilibrium constant
 of the reaction.
of the reaction.
The equation for
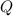 is quite similar to that for
is quite similar to that for
 . The difference between the two is that
. The difference between the two is that
 requires equilibrium concentrations, while
requires equilibrium concentrations, while
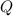 can be calculated even when the system is on its way to equilibrium.
can be calculated even when the system is on its way to equilibrium.
For this reaction,
![\displaystyle Q = \rm ([CS_2]\cdot [H_2]^(4))/([CH_4]\cdot [H_2S]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/pn1mj9gvup9f0o4rue6wv64ff8a2uedytm.png) .
.
Given these concentrations,
![\displaystyle Q = \rm ([CS_2]\cdot [H_2]^(4))/([CH_4]\cdot [H_2S]^(2)) =(1.51* (1.08)^(4))/(1.15* (1.20)^(2)) \approx 1.72](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/tbnle52llvgm2ulbi058j78u2pi8u162f3.png) .
.
The question states that at
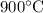 ,
,
 . Assume that currently this system is also at
. Assume that currently this system is also at
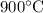 . (The two temperatures need to be the same since the value of
. (The two temperatures need to be the same since the value of
 depends on the temperature.)
depends on the temperature.)
It turns out that
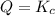 . What does this mean?
. What does this mean?
- First, the system isn't at equilibrium.
- Second, if there's no external changes, the system will continue to move towards the equilibrium. Temperature might change. However, eventually
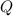 will be equal to
will be equal to
 , and the system will achieve equilibrium.
, and the system will achieve equilibrium.
In which direction will the system move? At this moment,
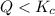 . As time proceeds, the value of
. As time proceeds, the value of
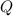 will increase so that it could become equal to
will increase so that it could become equal to
 . Recall that
. Recall that
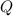 is fraction.
is fraction.
![\displaystyle Q = \rm ([CS_2]\cdot [H_2]^(4))/([CH_4]\cdot [H_2S]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/pn1mj9gvup9f0o4rue6wv64ff8a2uedytm.png)
When the value of
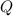 increases, either its numerator becomes larger or its denominator becomes smaller, or both will happen at the same time. However,
increases, either its numerator becomes larger or its denominator becomes smaller, or both will happen at the same time. However,
- Concentrations on the numerator of
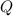 are those of the products;
are those of the products; - Concentrations on the denominator of
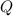 are those of the reactants.
are those of the reactants.
As time proceeds,
- the concentration of the products will increase, while
- the concentration of the reactants will decrease.
In other words, the equilibrium will move towards the products.