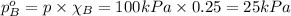Answer:
The partial pressure of component A and B is 75 kPa and 25kPa respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
Total pressure of ideal gas mixture = 100kPa
Mole fraction of component B,
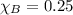
Mole fraction of component A ,
As we know sum of all mole fraction in a mixture is equal to zero.
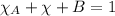
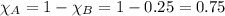
For partial pressure of each component we will apply Dalton's law of partial pressure:
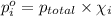
Partial pressure of component a in a mixture:
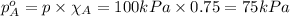
Partial pressure of component a in a mixture: