Answer:
Velocity is 2.17 m/s at an angle of 9.03° above X-axis.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of object 1 , m₁ = 300 g = 0.3 kg
Mass of object 2 , m₂ = 400 g = 0.4 kg
Initial velocity of object 1 , v₁ = 5.00i-3.20j m/s
Initial velocity of object 2 , v₂ = 3.00j m/s
Mass of composite = 0.7 kg
We need to find final velocity of composite.
Here momentum is conserved.
Initial momentum = Final momentum
Initial momentum = 0.3 x (5.00i-3.20j) + 0.4 x 3.00j = 1.5 i + 0.24 j kgm/s
Final momentum = 0.7 x v = 0.7v kgm/s
Comparing
1.5 i + 0.24 j = 0.7v
v = 2.14 i + 0.34 j
Magnitude of velocity
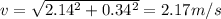
Direction,
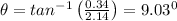
Velocity is 2.17 m/s at an angle of 9.03° above X-axis.