Answer:
The required answer is
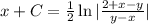 .
.
Explanation:
The given differential equation is
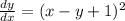
Substitute u=x-y+1 in the above equation.
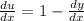
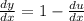
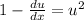
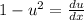
Using variable separable method, we get
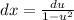
Integrate both the sides.
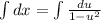
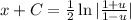
![[\because \int (dx)/(a^2-x^2)=(1)/(2a)\\|(a+x)/(a-x)|+C]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/y6hoik68csivu15cdgix5roetjiec380th.png)
Substitute u=x-y+1 in the above equation.
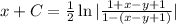
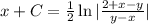
Therefore the required answer is
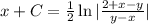 .
.