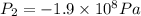Answer:
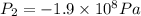
Step-by-step explanation:
As it is given that flow rate in the pipe is 20 cm^3/s
so we have
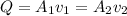
at the upper end the area is given as
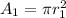
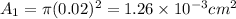
Also at the other end
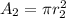
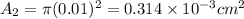
now the speed at two ends is given as
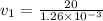
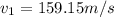
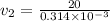
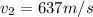
now by Bernoulli's theorem we have
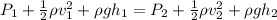
now we have
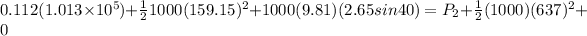
Now we have