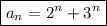a. This recurrence is of order 2.
b. We're looking for a function
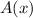 such that
such that
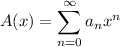
Take the recurrence,
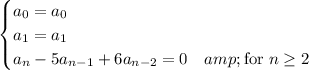
Multiply both sides by
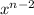 and sum over all integers
and sum over all integers
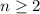 :
:
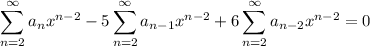
Pull out powers of
 so that each summand takes the form
so that each summand takes the form
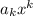 :
:
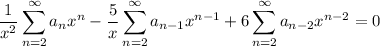
Now shift the indices and add/subtract terms as needed to get everything in terms of
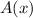 :
:
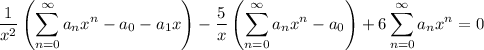
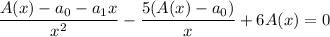
Solve for
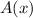 :
:
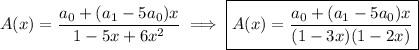
c. Splitting
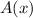 into partial fractions gives
into partial fractions gives
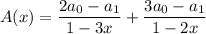
Recall that for
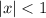 , we have
, we have
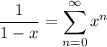
so that for
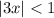 and
and
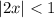 , or simply
, or simply
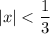 , we have
, we have
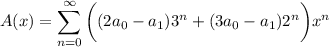
which means the solution to the recurrence is
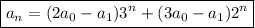
d. I guess you mean
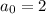 and
and
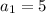 , in which case
, in which case
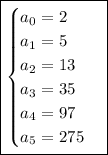
e. We already know the general solution in terms of
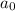 and
and
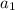 , so just plug them in:
, so just plug them in: