Step-by-step explanation:
We need to find the speed of an electron that has fallen through a potential difference of 125 volts. It can be calculated using the De-broglie hypothesis as :
(a) V = 125 volts
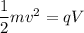
Where
v = speed of electron
V is potential difference
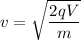
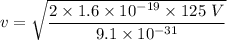
v = 6629935.44 m/s

(b) V = 125 megavolts
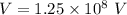
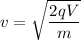
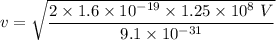

Hence, this is the required solution.