Answer : The volume of the sample after the reaction takes place is, 15.93 liters.
Explanation : Given,
Moles of
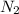 = 0.13 mole
= 0.13 mole
Moles of
 = 0.26 mole
= 0.26 mole
Initial volume of gas = 23.9 L
First we have to calculate the moles of
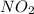 gas.
gas.
The balanced chemical reaction is :
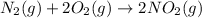
From the balanced reaction, we conclude that
As, 1 mole of
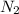 react with 2 moles of
react with 2 moles of
 to give 2 moles of
to give 2 moles of
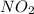 .
.
So, 0.13 mole of
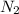 react with
react with
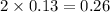 moles of
moles of
 to give
to give
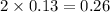 moles of
moles of
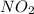 .
.
According to the Avogadro's Law, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas at constant pressure and temperature.
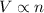
or,
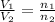
where,
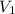 = initial volume of gas = 23.9 L
= initial volume of gas = 23.9 L
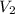 = final volume of gas = ?
= final volume of gas = ?
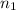 = initial moles of gas = 0.13 + 0.26 = 0.39 mole
= initial moles of gas = 0.13 + 0.26 = 0.39 mole
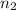 = final moles of gas = 0.26 mole
= final moles of gas = 0.26 mole
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get the final temperature of the gas.
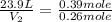
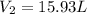
Therefore, the volume of the sample after the reaction takes place is, 15.93 liters.