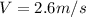Answer: (A) 26kgm/s (B) 2.6m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
This problem is a good example of an inelastic collision, in which the elements that collide remain together after the collision, and althogh the kinetic energy is not conserved, the linear momentum
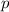 does.
does.
Thus:
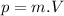 (1)
(1)
Where
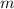 is the mass and
is the mass and
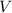 the velocity.
the velocity.
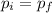 (2)
(2)
Where
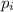 is the initial momentum and
is the initial momentum and
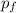 the final momentum.
the final momentum.
(A) Momentum of the two fish system after the smaller fish has been swallowed
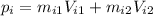 (3)
(3)
Where
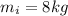 is the initial mass (mass of the big fish) and
is the initial mass (mass of the big fish) and
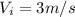 is the initial velocity of the big fish,
is the initial velocity of the big fish,
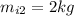 is the initial mass of the small fish and
is the initial mass of the small fish and
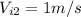 is the initial velocity of the small fish.
is the initial velocity of the small fish.
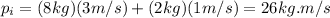 (4)
(4)
By the conservation of linear momentum:
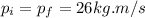 (5)
(5)
(B) Speed of the two fish system after the smaller fish has been swallowed
In this case we will focus on
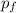 (after the "collision"):
(after the "collision"):
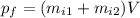 (6)
(6)
Where
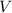 is the velocity of the system of both fish.
is the velocity of the system of both fish.
Finding
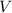 :
:
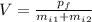 (7)
(7)
Solving (7) and remembering
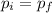 :
:
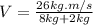 (8)
(8)
Finally: