To approximate the volume with 8 boxes, we have to split up the interval of integration for each variable into 2 subintervals, [0, 1] and [1, 2]. Each box will have midpoint
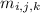 that is one of all the possible 3-tuples with coordinates either 1/2 or 3/2. That is, we're sampling
that is one of all the possible 3-tuples with coordinates either 1/2 or 3/2. That is, we're sampling
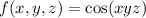 at the 8 points,
at the 8 points,
(1/2, 1/2, 1/2)
(1/2, 1/2, 3/2)
(1/2, 3/2, 1/2)
(3/2, 1/2, 1/2)
(1/2, 3/2, 3/2)
(3/2, 1/2, 3/2)
(3/2, 3/2, 1/2)
(3/2, 3/2, 3/2)
which are captured by the sequence
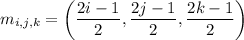
with each of
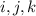 being either 1 or 2.
being either 1 or 2.
Then the integral of
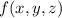 over
over
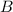 is approximated by the Riemann sum,
is approximated by the Riemann sum,
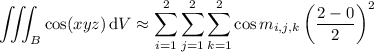
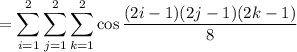
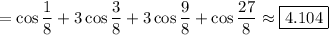
(compare to the actual value of about 4.159)