Answer:
Initially
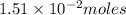 of nitrogen dioxide were in the container .
of nitrogen dioxide were in the container .
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of the container at low pressure and at room temperature =
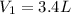
Number of moles in the container =
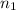
After more addition of nitrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature.
Volume of the container after addition =
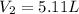
Number of moles in the container after addition=
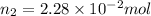
Applying Avogadro's law:
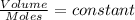 (at constant pressure and temperature)
(at constant pressure and temperature)
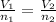
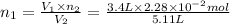
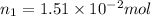
Initially
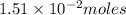 of nitrogen dioxide were in the container .
of nitrogen dioxide were in the container .