Answer:
The van't Hoff factor for sodium chloride in X is 1.9 .
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of liquid x = 950 g = 0.950 kg
When 282 g of glycine are dissolved in 950 g of a certain mystery liquid X.
Depression in freezing point of the solution
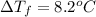
Molality of the solution = m
The van't Hoff factor for glycine (non ionic) in liquid X= i =1
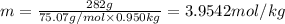
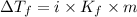
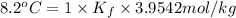
The value of molal depression constant for liquid X:
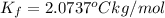 ..(1)
..(1)
Now 282. g of sodium chloride are dissolved in the same mass of X.
Depression in freezing point of the NaCl solution
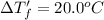
Molality of the NaCl solution = m'
The van't Hoff factor for NaCl(ionic) in liquid X= i'
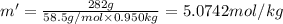
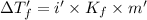
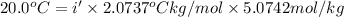
i = 1.9007 ≈ 1.9
The van't Hoff factor for sodium chloride in X is 1.9 .