Step-by-step explanation:
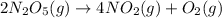
Rate of the reaction ,k=
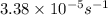
Half life of the
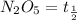
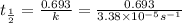 (first order kinetics)
(first order kinetics)
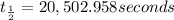
Half life of the
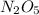 is 20,502.958 seconds.
is 20,502.958 seconds.
Integrated rate equation for first order kinetics in gas phase is given as:
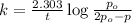
p= pressure of the gas at given time t.
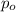 = Initial pressure of the gas
= Initial pressure of the gas
(i) When, t = 50 sec
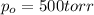
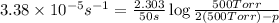
p = 500.49 Torr
(ii)When, t = 20 min = 1200 sec
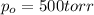
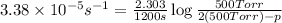
p = 519.83 Torr