Answer:
The value of the dissociation constant will be:
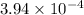 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
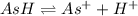
At ,t= 0 c 0 0
At eq'm (c-x) x x
Concentration of aspirin = c
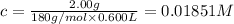
Expression for dissociation constant will be given as:
![K_a=([H^+][As^+])/([AsH])=(x* c)/((c-x))=(x^2)/((c-x))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zyk0utf616giw5ip857safiurlhzvpofq2.png) ..(1)
..(1)
The pH of the solution = 2.60
The pH of the solution is due to free hydrogen ions whcih come into solution after partial dissociation of aspirin.
![pH=2.60=\log[H^+]=-\log[x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/aguzjq5wxlrcx08eblr4rpbzwx6tmyo9fe.png)
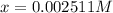
Putting value of x in (1).
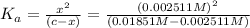
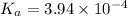
The value of the dissociation constant will be:
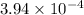 .
.