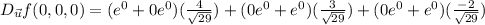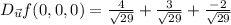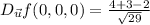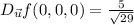Answer:
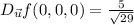
Explanation:
We need to find the directional derivative of the function at the given point in the direction of the vector v.
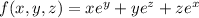 ,point (0, 0, 0) and
,point (0, 0, 0) and
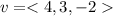
By Theorem: If f is a differentiable function of x , y and z , then f has a directional derivative for any unit vector
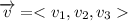 and
and
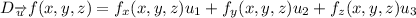
where
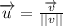
since,
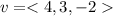
then
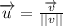
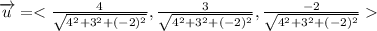
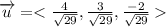
The partial derivatives are
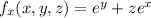
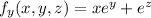
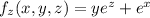
Then the directional derivative is
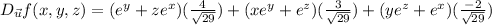
so, directional derivative at point (0,0,0)