Answer:
ΔH/mol H₂O = 55346 J/mol H₂O =55.346 kJ/mol H₂O
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction that occurs in this case is:
Ba(OH)₂ + 2 HCl ----> BaCl₂ + 2 H₂O
The measurement and calculation of the amounts of heat exchanged by a system is called calorimetry. The equation that allows calculating these exchanges is:
Q=c*m*ΔT
where Q is the heat exchanged for a body of mass m, constituted by a substance whose specific heat is c, and ΔT is the temperature variation experienced.
In this case:
- c=4.184
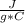
- mass solution = mass Ba(OH)₂ + mass HCl
Given that the solution has the same density as water (1.00
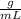 ) then the mass of Ba (OH)₂ and HCl can be calculated as:
) then the mass of Ba (OH)₂ and HCl can be calculated as:
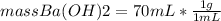
mass Ba(OH)₂=70 g
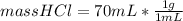
mass HCl=70 g
mass solution = 70 g of Ba(OH)₂ + 70 g of HCl
mass solution = 140 g
Another way to calculate the mass of the solution is:
The total volume is the sum of the individual volumes:
total volume= volume of Ba(OH)₂ + volume of HCl = 70 mL + 70 mL
total volume= 140 mL
Given that the solution has the same density as water (1.00
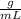 ) then
) then
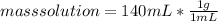
mass solution = 140 g
- ΔT=28.70° C - 24.07 °C= 4.63° C
Then
Q = 140 g* 4.184
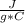 *4.63° C =2712 J
*4.63° C =2712 J
By reaction stochetry (that is, by the relationships between the molecules or elements that make up the reactants and reaction products) 2 moles of HCl produce 2 moles of H2O.
Then
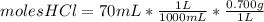
moles HCl=0.049
The rule of three or is a way of solving problems of proportionality between three known values and an unknown value, establishing a relationship of proportionality between all of them. That is, what is intended with it is to find the fourth term of a proportion knowing the other three. Remember that proportionality is a constant relationship or ratio between different magnitudes.
If the relationship between the magnitudes is direct, that is, when one magnitude increases, so does the other (or when one magnitude decreases, so does the other) , the direct rule of three must be applied. To solve a direct rule of three, the following formula must be followed:
a ⇒ b
c ⇒ x
So
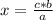
In this case: If 2 moles of H2O are formed if 2 moles of HCl react, how many moles of H2O will be formed if 0.049 moles of HCl react?
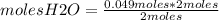
moles H2O=0.049 moles
Now
ΔH/mol H₂O =
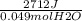
ΔH/mol H₂O = 55346 J/mol H₂O =55.346 kJ/mol H₂O