Answer: The specific heat of substance A is 1.1 J/g°C
Step-by-step explanation:
When substance A is mixed with substance B, the amount of heat released by substance B (initially present at high temperature) will be equal to the amount of heat absorbed by substance A (initially present at low temperature)
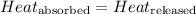
The equation used to calculate heat released or absorbed follows:
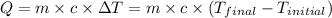
![m_1* c_1* (T_(final)-T_1)=-[m_2* c_2* (T_(final)-T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bm2kxludvecqgwsul6e5upktie71evfnq2.png) ......(1)
......(1)
where,
q = heat absorbed or released
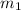 = mass of substance A = 6.07 g
= mass of substance A = 6.07 g
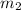 = mass of substance B = 26.1 g
= mass of substance B = 26.1 g
tex]T_{final}[/tex] = final temperature = 47.0°C
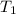 = initial temperature of substance A = 20.7°C
= initial temperature of substance A = 20.7°C
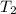 = initial temperature of substance B = 52.8°C
= initial temperature of substance B = 52.8°C
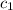 = specific heat of substance A = ?
= specific heat of substance A = ?
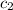 = specific heat of substance B = 1.17 J/g°C
= specific heat of substance B = 1.17 J/g°C
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
![6.07* c_1* (47-20.7)=-[26.1* 1.17* (47-52.8)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pfiyyfkmeyskq36v9sksgb6sskok7d4ctq.png)
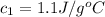
Hence, the specific heat of substance A is 1.1 J/g°C