Answer : The equilibrium concentrations of
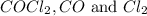 are, 0.2646, 0.0584 and 0.0584.
are, 0.2646, 0.0584 and 0.0584.
Explanation : Given,
Moles of
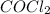 = 0.323 mole
= 0.323 mole
Volume of solution = 1 L
Initial concentration of
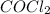 = 0.323 M
= 0.323 M
Let the moles of
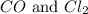 be, 'x'. So,
be, 'x'. So,
Concentration of
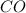 = x M
= x M
Concentration of
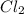 = x M
= x M
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
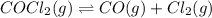
Initial conc. 0.323 M 0 0
At eqm. conc. (0.323-x) M (x M) (x M)
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([CO][Cl_2])/([COCl_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/g3ihemxb2m1r7d5xpaqvb68alpnws7llu4.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
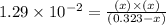
By solving the term 'x', we get :
x = 0.0584
Thus, the concentrations of
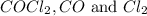 at equilibrium are :
at equilibrium are :
Concentration of
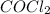 = (0.323-x) M = (0.323-0.0584) M = 0.2646 M
= (0.323-x) M = (0.323-0.0584) M = 0.2646 M
Concentration of
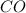 = x M = 0.0584 M
= x M = 0.0584 M
Concentration of
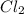 = x M = 0.0584 M
= x M = 0.0584 M
Therefore, the equilibrium concentrations of
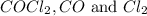 are, 0.2646, 0.0584 and 0.0584.
are, 0.2646, 0.0584 and 0.0584.