Answer:
7.8286×10²¹ particles.
Step-by-step explanation:
First we need to calculate the total molar mass of the compound, in this case:
Potassium (K) = 39.1 g/mol × 2 = 78.2 +
Oxigen (O) = 16 g/mol × 1 = 16
Total(K₂O) = 94.2 g/mol
Then, we calculate the number of moles of the compound in the sample, this is done dividing de mass of the sample by the molar mass:
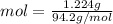
mol = 0.013 moles in our sample.
Finally, we calculate the total number of particles. The costant known as Avogadro number (6.022×10²³) is the number of particles or atoms contained in a mole of any substance. We need to multiply the number of moles by the Avogadro number.
particles = 0.013 mol × (6.022×10²³ particles/mol) = 7.8286×10²¹ particles.