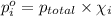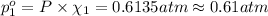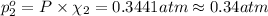Step-by-step explanation:
Moles of nitrogen gas =
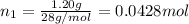
Moles of oxygen gas =
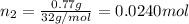
Mole fraction of nitrogen gas=
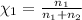
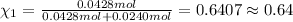
Mole fraction of oxygen gas=
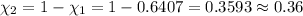
Total umber of moles in container :
n =
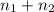 = 0.0428 mol + 0.0240 mol = 0.0668 mol
= 0.0428 mol + 0.0240 mol = 0.0668 mol
Volume of the container = V = 1.65 L
Temperature of the container = T = 15°C = 288.15 K
Total pressure in the container = P
Using an ideal gas equation:
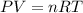
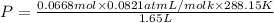
P = 0.9577 atm
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas =
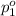
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas =
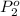
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas and oxygen gas can be calculated by using Dalton's law of partial pressure: