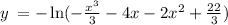Answer:
The solution is
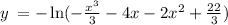
Explanation:
We need to find the solution of IVP for differential equation
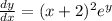 when
when
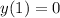
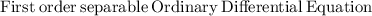
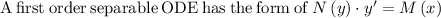
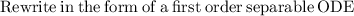
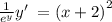
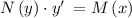
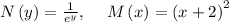
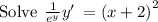
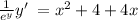
Integrate both the sides with respect to dx
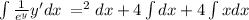
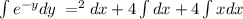
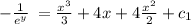
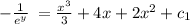
Since, IVP is y(1)=0
put x=1 and y=0 in above equation
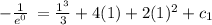
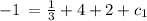
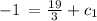
add both the sides by
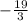
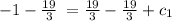
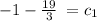
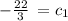
so,
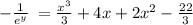
Multiply both the sides by '-1'
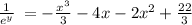
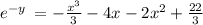
Take natural logarithm both the sides,
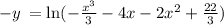
Multiply both the sides by '-1'
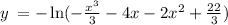
Therefore, the solution is