Answer:
Depending on the definition of "standard" conditions, the volume of O₂ required here will be either
- 43.1 L if the STP volume is 22.4 L/mol, or
- 43.7 L if the STP volume is 22.7 L/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Relative atomic mass data from a modern periodic table:
How many moles of iron Fe in that 35.8 gram of iron metal?
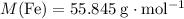 .
.
 .
.
How many moles of oxygen gas will be required?
Consider the ratio between the coefficient of Fe and that of
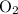 in the equation:
in the equation:
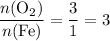 .
.
As a result,
 .
.
What's the volume of that
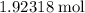 of oxygen gas under STP?
of oxygen gas under STP?
One mole of an ideal gas occupies a volume 22.4 Liters under STP (or 22.7 liters in certain textbooks.) The volume of an ideal gas is directly related to the number of moles of particles in this gas. Assume that oxygen acts like an ideal gas under STP. As a result, 1.92318 moles of oxygen will occupy a volume of either
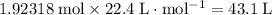 or
or
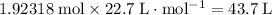 .
.