Answer:
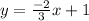
Explanation:
Linear equations are typically organized in slope-intercept form:
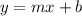 . Here's what the variables mean:
. Here's what the variables mean:
y = the y-coordinate
m = the slope
x = the x=coordinate
b = the y-intercept (what y is equal to when the line crosses the y-axis)
First, we need to calculate the slope of the line (m). The slope is the
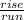 of the line, or in other words, the change in y over the change in x. We can find this by just looking at the graph, between the two given points. For 3 spaces the line travels to the right, it travels downward 2 spaces. Therefore, the slope of the line is
of the line, or in other words, the change in y over the change in x. We can find this by just looking at the graph, between the two given points. For 3 spaces the line travels to the right, it travels downward 2 spaces. Therefore, the slope of the line is
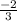 .
.
We can also calculate this using the formula
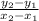 by using two points that fall on the line,
by using two points that fall on the line,
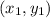 and
and
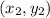 . Here, we can use the points (-3,3) and (0,1).
. Here, we can use the points (-3,3) and (0,1).
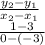
Two negatives make a positive
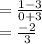
Then, we need to find the y-intercept of the line (b). We can find this by, again, looking at the graph. The line crosses the y-axis when y is equal to 1, so the y-intercept of the line is 1.
Now, we plug our calculated values back into the original equation:
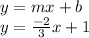
I hope this helps!