Answer: The amount of heat released is 56 MJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
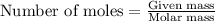
Given mass of
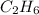 = 12 kg = 12000 g (Conversion factor: 1 kg = 1000 g)
= 12 kg = 12000 g (Conversion factor: 1 kg = 1000 g)
Molar mass of
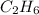 = 30 g/mol
= 30 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
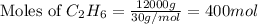
The chemical reaction for hydrogenation of ethene follows the equation:
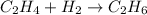
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
When 1 mole of ethane releases 140 kJ of heat.
So, 400 moles of ethane will release =
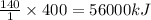 of heat.
of heat.
Converting this into Mega joules, using the conversion factor:
1 MJ = 1000 kJ
So,
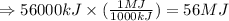
Hence, the amount of heat released is 56 MJ.