Answer: y < 1
Explanation:
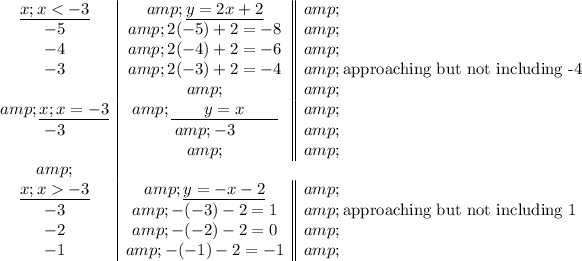
The first function has the range of y < -4
The second function has the range of y = -3
The third function has the range of y < 1
The largest y-value is 1 and the smallest y-value is -∞, therefore the range (y-values) are from -∞ to 1 → y < 1