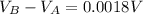Answer:
0.0018 V
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the law of conservation of energy, the kinetic energy gained by the particle is equal to the electric potential energy lost:
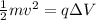
where
 is the mass of the particle
is the mass of the particle
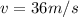 is the final speed of the particle
is the final speed of the particle
q = -2.7 C is the charge
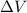 is the potential difference between the two points
is the potential difference between the two points
Solving for
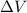 , we find
, we find
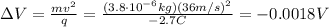
The particle has been accelerated by this potential difference: since it is a negative charge, it means that the particle has moved from a point at lower potential towards a point of higher potential.
So, since the initial point is A and the final point is B, the result is