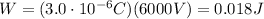Answer:
0.018 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The work done to bring the charge from infinity to point P is equal to the change in electric potential energy of the charge - so it is given by
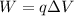
where
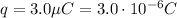 is the magnitude of the charge
is the magnitude of the charge
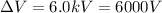 is the potential difference between point P and infinity
is the potential difference between point P and infinity
Substituting into the equation, we find