Answer:
Both objects are packed equally tightly.
Step-by-step explanation:
For Substance R we have
mass = 10 g
Volume = 22 cubic cm
So we know that density is defined as
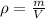
here we have
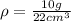
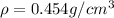
For substance S we have
mass = 25 g
Volume = 55 cubic cm
So we know that density is defined as
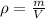
here we have
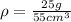
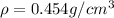
So here both have same density
so correct answer would be
Both objects are packed equally tightly.