Answer:
Ionic bonds hold charged particles in solid NaCl together, such that they are unable to move or conduct electricity.
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider an electric current that flows through a conductor: charge moves in a uniform direction from one end of the conductor towards the other.
Thus, there are two conditions for a substance to conduct electricity:
- The substance shall contain charged particles, and
- These charged particles shall be free to move across the substance.
A conductor of electricity shall meet both requirements.
Now, consider the structure of solid NaCl
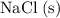 . NaCl is an ionic compound. It contains an ocean of oppositely charged ions:
. NaCl is an ionic compound. It contains an ocean of oppositely charged ions:
- Positive
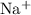 ions, and
ions, and - Negative
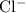 ions.
ions.
Ions carry charge. Thus, solid NaCl contains charged particles and satisfies the first condition.
Inside solid NaCl
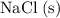 , electrostatic attractions ("ionic bonds") between the oppositely charged ions hold these ions in rigid ionic lattices. These ions are unable to move relative to each other. As a result, they cannot flow through the solid to conduct electricity. Under solid state, NaCl is unable to satisfy the second condition.
, electrostatic attractions ("ionic bonds") between the oppositely charged ions hold these ions in rigid ionic lattices. These ions are unable to move relative to each other. As a result, they cannot flow through the solid to conduct electricity. Under solid state, NaCl is unable to satisfy the second condition.
As a side note, melting NaCl into a liquid breaks the ionic bonds and free the ions from the lattice. Liquid NaCl is a conductor of electricity.