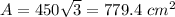Answer:
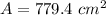
Explanation:
we know that
The area of a regular hexagon is equal to the area of six equilateral triangles
Applying the law of sines
The area of six equilateral triangles is equal
![A=6[(1)/(2)b^(2)sin(60)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/zk2qefgnecbiiab8cz2as59u1w6gzoqoz5.png)
where
b is the side length of the regular hexagon
we have
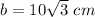
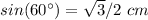
substitute
![A=6[(1)/(2)(10√(3))^(2)(√(3)/2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/3tbmmxog0iifhgwxv5be6l9o1a1om1t529.png)