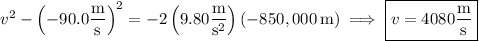Before it hits the sand bed, the meteorite is accelerating uniformly with
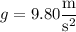 , so that its speed
, so that its speed
 satisfies
satisfies
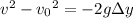
where
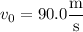 is its initial speed and
is its initial speed and
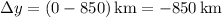 is its change in altitude. Notice that we're taking the meteorite's starting position in the atmosphere to be the origin, and the downward direction to be negative. Now,
is its change in altitude. Notice that we're taking the meteorite's starting position in the atmosphere to be the origin, and the downward direction to be negative. Now,