Answer:
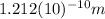
Step-by-step explanation:
The de Broglie wavelength
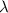 is given by the following formula:
is given by the following formula:
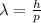 (1)
(1)
Where:
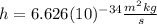 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
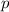 is the momentum of the atom, which is given by:
is the momentum of the atom, which is given by:
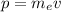 (2)
(2)
Where:
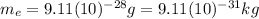 is the mass of the electron
is the mass of the electron
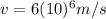 is the velocity of the electron
is the velocity of the electron
This means equation (2) can be written as:
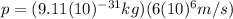 (3)
(3)
Substituting (3) in (1):
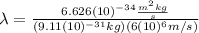 (4)
(4)
Now, we only have to find
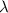 :
:
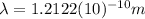 >>> This is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron
>>> This is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron