ANSWER
A solution of the radical equation that does not satisfy the original radical equation.
Step-by-step explanation
An extraneous is the solution that does not satisfy the original equation.
For instance, given the radical equation:
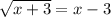
We square both sides to get:
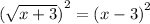
We expand to get;
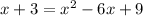
We write in standard quadratic forms:
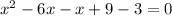
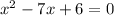
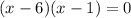
This implies that;
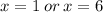
When we substitute x= 6 into the equation, we get;
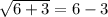
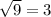
This statement is true.
However when we substitute x=1, we get:
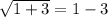
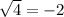 This statement is false.
This statement is false.
Hence x=1 u s referred to as an extraneous solution.