Answer:
Part 1)
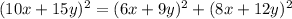
Part 2) The answer in the procedure
Explanation:
Part 1)
we know that
Applying the Pythagoras Theorem
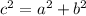
we have
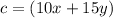
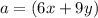
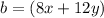
substitute the values
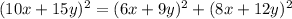
Part 2) Transform each side of the equation to determine if it is an identity
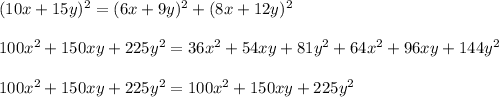
The left side is equal to the right side
therefore
Is an identity