Answer: The frequency decreases.
Step-by-step explanation:
The Compton Effect is related to an experiment the American physicist Arthur H. Compton made, consisting in the scattering of photons from electrons, proving photons have momentum.
In additon, Compton proved that when a photon collides with a free electron, the photon loses part of its energy
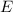 , which is given by the following equation:
, which is given by the following equation:
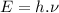 (1)
(1)
Where:
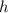 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
 is the frequency of the photon
is the frequency of the photon
So, the energy of the photon is directly proportional to its frequency, therefore, if energy decreases in the Compton effect, the frequency decreases as well.
This also means, the photon wavelength increases (because there is an inverse relation between frequency and wavelength)
It is important to note the frequency (or wavelength) of the scattered radiation depends only on the scattering angle
 , which is an important element in the Compton Shift
, which is an important element in the Compton Shift
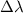 equation:
equation:
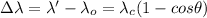
Where:
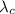 is a constant whose value is given by
is a constant whose value is given by
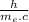 , being
, being
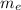 the mass of the electron and
the mass of the electron and
 the speed of light in vacuum.
the speed of light in vacuum.
Hence, the correct option is B.