Answer:
c) 10 microns/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The drift velocity (the velocity of the current) of the electrons in a wire is given by
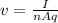
where
I is the current
n is the electron number density (the number of electrons per unit volume)
A is the cross-sectional area of the wire
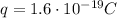 is the charge of one electron
is the charge of one electron
Taking a current of
I = 1 A
in a wire of radius r = 1 mm (0.001 m), so with cross-sectional area
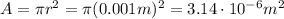
made of copper, whose electron density number is around
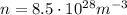
we find
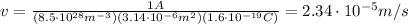
which means that the closest estimate is
c) 10 microns/s