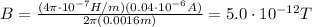Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We can think the axons as current-carrying wires
The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying wire is
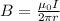
where
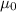 is the vacuum permeability
is the vacuum permeability
I is the current
r is the distance from the wire
In this problem we have
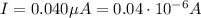
r = 1.6 mm = 0.0016 m
So the strength of the magnetic field is