Answer:
Approximately 3 photons
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy of a photon at the peak of visual sensitivity is given by:
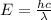
where
h is the Planck constant
c is the speed of light
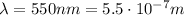 is the wavelength of the photon
is the wavelength of the photon
Substituting into the formula,
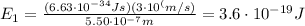
This is the energy of one photon. The human eye can detect an amount of energy of
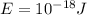
So the amount of photons contained in this energy is
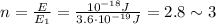
so approximately 3 photons.