Answer: Option C
domain: x is a real number; range: y
Explanation:
We have the function
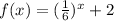
Note that f(x) is an exponential function.
By definition the exponential functions of the form
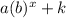 have as domain all real numbers and as range y if
have as domain all real numbers and as range y if
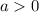 ,
,
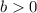
Where a is the main coefficient, b is the base and k is the vertical displacement.
In this case
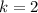 ,
,
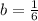 ,
,
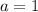
Therefore the domain of f(x) is all real numbers and the range of f(x) is
y > 2