Answer:
It has one proton instead of a neutron (beta-minus decay) or a neutron instead of a proton (beta-plus decay)
Step-by-step explanation:
- In a beta-minus decay, a neutron in the nucleus turns into a proton, emitting an electron and an anti-neutrino:
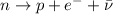
In this process, therefore, the final nucleus will have a proton instead of a neutron. This means that the atomic number Z (number of protons) will increase by one, while the mass number A (number of protons+neutrons) will remain the same.
- In a beta-plus decay, a proton in the nucleus turns into a neutron, emitting a positron and a neutrino:
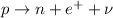
In this process, therefore, the final nucleus will have a neutron instead of a proton. This means that the atomic number Z (number of protons) will decrease by one, while the mass number A (number of protons+neutrons) will remain the same.