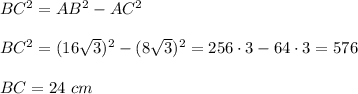Answer:
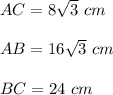
Explanation:
Consider right triangle ADH ( it is right triangle, because CH is the altitude). In this triangle, the hypotenuse AD = 8 cm and the leg DH = 4 cm. If the leg is half of the hypotenuse, then the opposite to this leg angle is equal to 30°.
By the Pythagorean theorem,
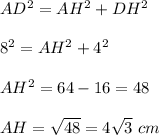
AL is angle A bisector, then angle A is 60°. Use the angle's bisector property:
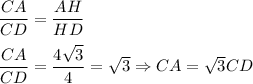
Consider right triangle CAH.By the Pythagorean theorem,
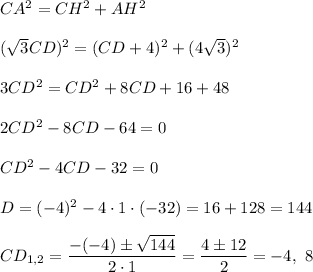
The length cannot be negative, so CD=8 cm and
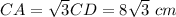
In right triangle ABC, angle B = 90° - 60° = 30°, leg AC is opposite to 30°, and the hypotenuse AB is twice the leg AC. Hence,
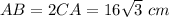
By the Pythagorean theorem,