Answer: sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
Acid rain is the result of changing the pH of gases and water present in the atmosphere, producing precipitation (rain or snow), whose pH is lower than natural rainfall (generally pH = 5).
This phenomenon occurs due to the effect of two gases: sulfur dioxide
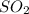 and nitrogen oxides
and nitrogen oxides
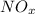 .
.
Sulfur dioxide is naturally emanated in volcanic eruptions, but it is also produced in large quantities by the metallurgical industry. While nitrogen oxides are emitted in conjunction with
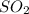 by factories, power plants and vehicles that work with petroleum products or burning coal.
by factories, power plants and vehicles that work with petroleum products or burning coal.
Then, these toxic gases interact with the water vapor present in the atmosphere, forming sulfuric acid and nitric acid, then these chemicals fall to the ground with the precipitation thus forming acid rain.