Answer:
Decreasing the cross-sectional area of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.
Increasing the resistivity of the material the wire is composed of will increase the resistance of the wire.
Increasing the length of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.
Step-by-step explanation:
The resistance of a piece of wire is given by:
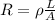
where
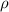 is the resistivity of the material
is the resistivity of the material
L is the length of the wire
A is the cross-sectional area of the wire
We notice that:
- The resistance of the wire is directly proportional to the resistivity of the material and the to the length of the wire
- The resistance of the wire is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the wire
This means the following are correct:
Decreasing the cross-sectional area of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.
Increasing the resistivity of the material the wire is composed of will increase the resistance of the wire.
Increasing the length of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.