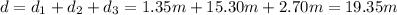(a) 18717 N
Newton's second law in this situation can be written as:
 (1)
(1)
where
T is the tension in the cable, pointing upward
W is the weight of the elevator+passengers, pointing downward
m is the mass of the elevator+passengers (1700 kg)
a is the acceleration of the system (1.20 m/s^2, upward)
The weight is equal to the product between the mass, m, and the gravitational acceleration, g:
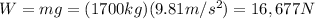
So now we can solve eq.(1) to find T, the tension in the cable:
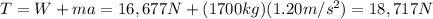
(b) 16677 N
In this situation, the elevator is moving with constant velocity: this means that its acceleration is zero,
a = 0
So Newton's second law becomes
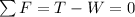
and so we find
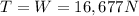
(c) 15657 N
During the deceleration phase, Newton's second law can be written as:
 (1)
(1)
Where the acceleration here points downward (because the elevator is decelerating), as the weight W, so we can write it as a negative number:
a = -0.600 m/s^2
we can solve the equation to find T, the tension in the cable:
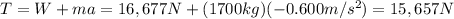
(d) 19.35 m, 0 m/s
Distance covered during the first part of the motion; we know that
u = 0 is the initial velocity
a = 1.20 m/s^2 is the acceleration
t = 1.50 s is the time
So the distance covered is given by
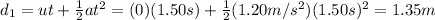
and the final velocity after this phase is
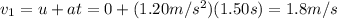
During the 2nd part of the motion, the elevator moves at constant speed of 1.8 m/s for t=8.50 s, so the distance covered here is
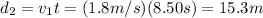
Finally, in the third part the elevator decelerates at a = -0.600 m/s^2 for t = 3.00 s. So, the distance covered here is
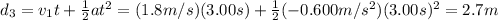
and the final velocity is
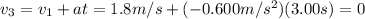
and the total distance covered is